Starlight Stadium spans four episodes that each tackle a different aspect of the human rights monitoring cycle. Episode 1 teaches the initial assessment of the human rights problem, Episode 2 teaches information gathering, Episode 3 teaches verification, analysis and report writing, and Episode 4 teaches advocacy. The lessons learned through these episodes can be used throughout your work as human rights monitors.
What episode should I play?
You can play each episode as many times as you’d like, and although they contribute to this series, they’re designed to be played as standalone episodes, too.
Each episode of Starlight Stadium teaches various aspects of human rights monitoring and application of principles, using consistent technological features throughout. To help decide which episode to play, and to understand the game’s core features, the following two .pdf documents are available for download:
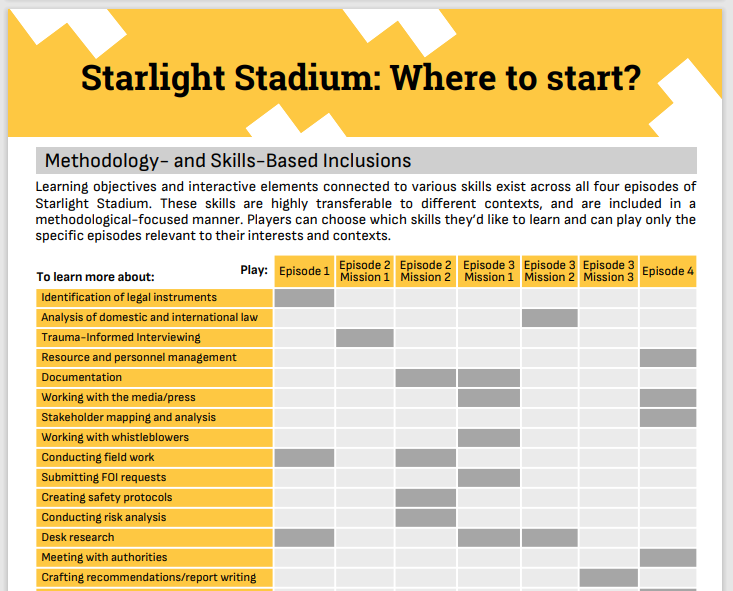
Overview, Content Mapping
This .pdf takes readers through an overview of the game and presents a mapping of relevant episodes related to various topics and human rights monitoring principles.

Core Features, Troubleshooting
This .pdf describes the core features of Starlight Stadium and presents various troubleshooting solutions.
Have you played Starlight Stadium?
If so, any feedback you could provide via this form would be greatly appreciated.
Click here to expand the Feedback Form
Learning Objectives
Based on ODIHR’s Human Rights Monitoring training curriculum, each of the four episodes of Starlight Stadium are linked to specific learning objectives that will reinforce your understanding of the human rights monitoring cycle. The learning objectives for each episode can be reviewed below:
Episode 1 – Initial Assessment of the Human Rights Problem
During Episode 1, you will:
- Understand incident security protocols.
- Learn the human rights standards found in some international conventions.
- Understand the nature of State obligation.
- Understand the principles of human rights (universality, inalienability, indivisibility, etc.).
- Understand the concept of limited or absolute rights.
- Learn about passwords, multi-factor authentication, email encryption, and physical security protocols.
Episode 2 – Information Gathering
During the scenes with Mr X, you will:
- Learn about when to use secure communication channels.
- Understand the different steps needed to conduct an interview, including planning and preparing for the interview, engaging with the interviewee, and explaining the interview process.
- Learn about the importance of informed consent.
- Understand when and how to use open-ended questions.
During the scenes with Toni, you will:
- Learn how to select a secure and comfortable location and consider who should be present.
- Learn about the PEACE model of interviewing.
- Encourage an uninterrupted narrative with open-ended questions.
- Understand how to implement a trauma-informed approach to an interview.
- Consider the victims’ needs and refer them to an appropriate service provider.
During the direct observation scenes, you will:
- Understand the importance of a risk assessment and how to undertake one
- Learn about the do’s and don’ts for preparing for an on-site observation.
- Understand how to document not just “what” is happening, but also “who” and “how”.
Episode 3 – Verification, Analysis, Report Writing
During verification, you will:
- Remember that verification is a precondition to analysis and one should never act on information that is not verified.
- Understand how the human rights monitoring principles apply to verification and are interconnected.
- Understand that for information to be verified, one must assess its source reliability, the information’s credibility, its consistency, and its coherence with the broader context.
- Understand it is important to consider the reliability of your sources of information when verifying.
- Be able to acknowledge your own personal biases in verifying (and analysing) information, when assessing how it fits into the context of the situation.
- Understand the various means through which information can be corroborated.
- Appraise information via cross-checking with multiple sources.
- Recall that digital methods can be used to verify information.
During analysis, you will:
- Comprehend the different components of analysis.
- Understand the importance of legality, legitimacy and proportionality tests on determining a human rights violation.
- Understand that the relevant actors/institutions and policies relating to the human rights problems being addressed must be identified.
- Understand the role that contextualisation plays in analysis.
- Understand how to assess the level of responsibility of the duty bearer.
- Understand that it is necessary to identify the legal/normative implications of the human rights problem.
- Understand how to draw conclusions on the human rights issue based on the result of the analysis.
During report writing, you will:
- Be able to effectively structure a human rights report based on six essential sections: Table of Contents, Executive Summary, Methodology, Findings, Recommendations, and Legal Framework.
- Recall the key content that goes into the Executive Summary and Methodology sections of a report.
- Be able to recognize SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Result-oriented/Relevant, Time-Bound) recommendations.
- Understand that key human rights monitoring principles must be mainstreamed throughout reporting.
- Understand the necessity for source confidentiality.
- Understand the importance of focusing the report on state actions.
- Understand the importance of including an intersectional perspective in your report.
Episode 4 – Advocacy
During Episode 4, you will:
- Get introduced to the definition of human rights advocacy: advocacy involves a wide variety of techniques, including direct or indirect pressure, politeness, humility, showing empathy for the interlocutor, praise and stressing mutual objectives or developing solutions together.
- Understand what stakeholder mapping is and how it can be used for advocacy purposes.
- Learn how to deliver key messages to stakeholders.
- Have the opportunity to implement an advocacy strategy while managing resources and capacity of your team.
- Learn to respond to new risks emerging from the increase of exposure.